Transition to cellular manufacturing processes made possible for manufacturer of composite parts with IONA
Manufacturing composite components for automotive applications typically follows one of two approaches; a low-volume, high-mix process (usually manual), or a high-volume, low-mix process (usually automated).
A manufacturer of composite parts for automotive applications (Manufacturer X) recognised the increasing desire for more customisable solutions. As this customisation was required in parts that were typically manufactured using high-volume processes, they sought to transition from a traditional production line to a cellular manufacturing process.
In a cellular manufacturing process, machines are grouped together based on the type of work they perform. This allows for a more efficient use of space and resources, and it also makes it easier to track and manage the production process. Cellular manufacturing processes also enable manufacturers to produce a variety of parts on the same machine making the process more flexible and able to deliver more customised products and outcomes.
The goal of this transition was to achieve the flexibility required to meet the ever-evolving demands of manufacturing today, whilst maintaining volume output and efficiencies, and reducing costs.
The Challenge
One area that Manufacturer X found to be particularly challenging to transition was the final trimming process.
Existing solutions for edge trimming involve either manual trimming or large-scale 5-axis CNC machines, which are costly and require significant set up time. While existing CNC machines offer high adaptability, their extensive setup time and high skill requirements makes them hard to scale and often required a high capital cost for Manufacturer X.
Another solution that has emerged are serial arm robotic solutions. These systems feature lower capital costs compared to CNC machines and exhibit a more gradual scalability as production volumes increase. However, for robotic trimming solutions they still also share the drawback of requiring significant setup time and are more suitable for repetitive operations.
The setup time associated with 5axis CNC machines or Serial Arm Robots is primarily due to the datuming process. This process primarily involves a skilled operator setting the datum (accurate location) of the fixture or part. The current skill level and process time of industrial trimming solutions often prevents manufacturers from adopting cellular production, forcing manufacturers to adopt batch or serial production. Manufacturer X understood that by reducing the time and deskilling the setup, the adoption of a cellular process could be achieved.
The Solution
Manufacturer X concluded that using robots for trimming offered an exceptional opportunity for them to customise their machinery according to a diverse range of products. It was clear that a solution to speed up the set-up process was required to realise this opportunity and embed trimming robots into the cellular manufacturing process.
IONA solved this issue by delivering a fast and precise method for aligning the robot’s frames (Base frame, Tool Centre Point) to a designated working frame, such as a fixture. IONA reduced the need for manual or semi-manual alignment, previously carried out using touch probes, and significantly reduced the set-up time. Not only this, but by being an automated fully integrated system, IONA also eliminated concerns around human errors in the set-up process.
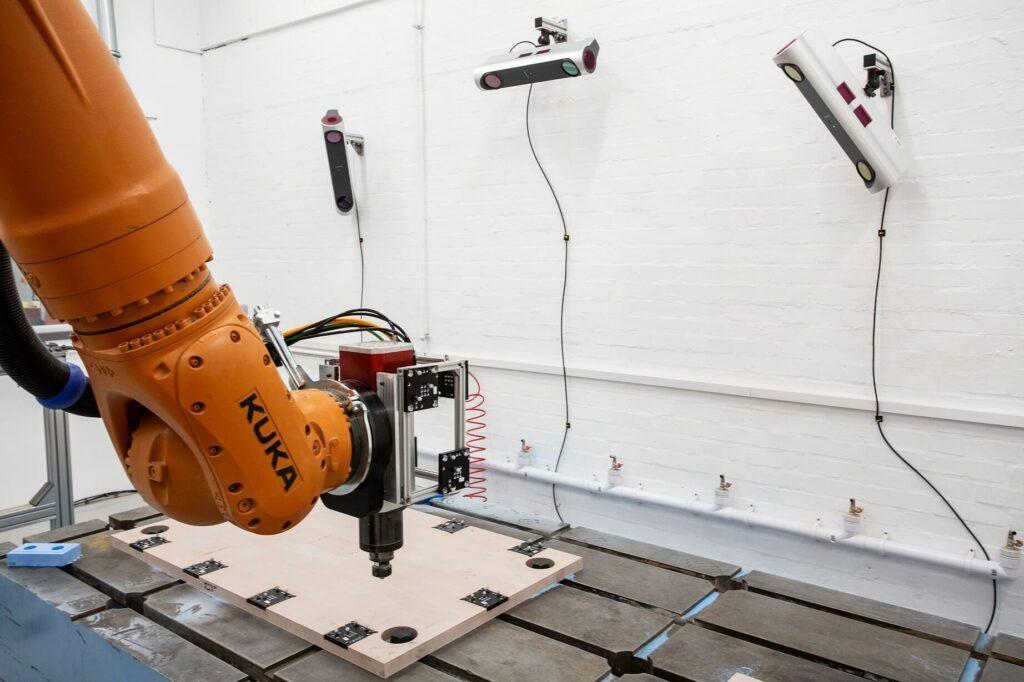
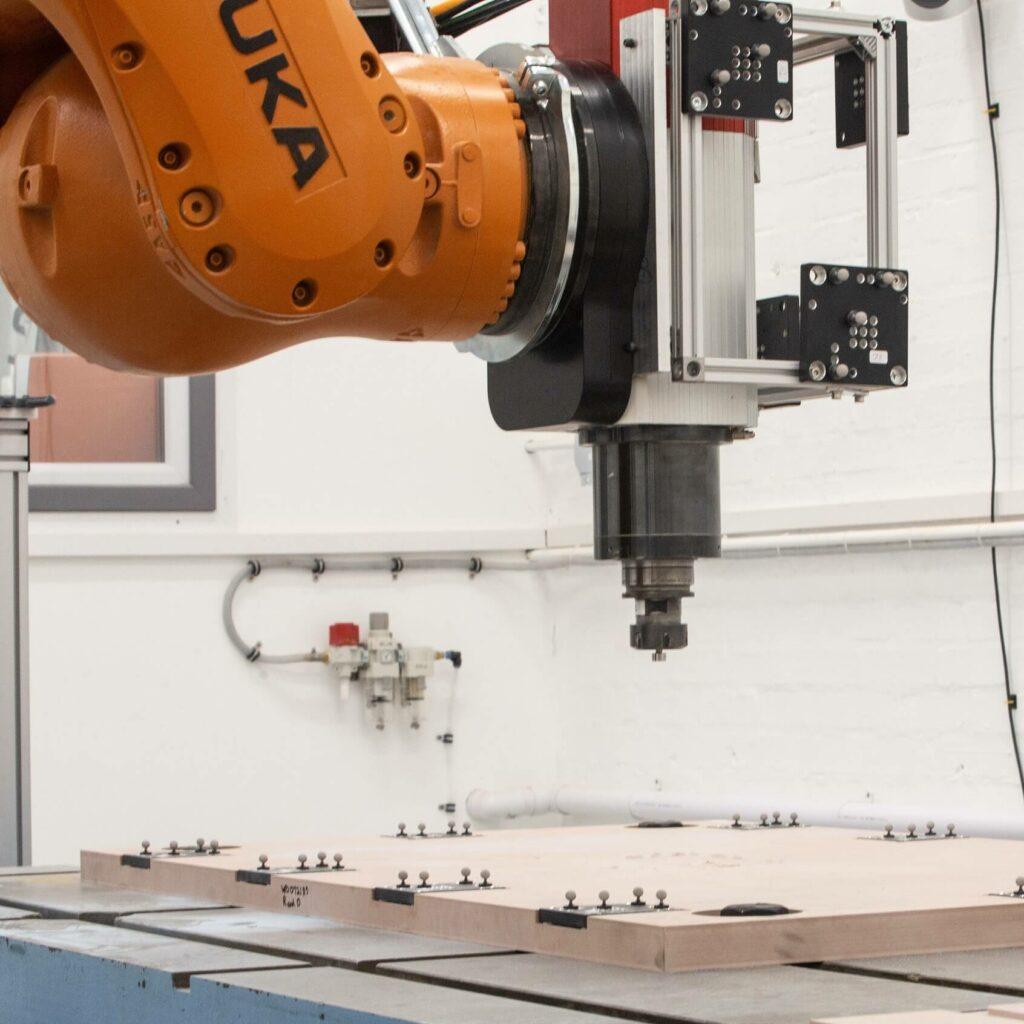
IONA is a scalable network of sensors providing metrology-grade data for industrial robots. The sensors (nodes) have been permanently deployed into the manufacturing environment allowing continuous data capture. With IONA, robot cells are no longer dedicated to a single part or a low mix of parts. IONA enables the possibility for any part and its associated fixture to be processed in any of Manufacturer X’s robotic trimming cells.
The benefits of implementing IONA to realise the cellular manufacturing process have proven to be significant. Not only has a new level of flexibility been achieved, but also the need for dedicated cells or machinery for low mix of parts has been eliminated, resulting in a reduction in overall capital expenditure for manufacturing facilities.
With IONA any part can be produced on any machine as the identification and alignment process is nearly instantaneous. This near-instantaneous adaptability enables manufacturers to make on-the-fly adjustments to their production schedule. As a result, higher machinery throughput can be achieved, generating greater value for the manufacturer, and increasing overall productivity. This newfound flexibility empowers manufacturing facilities to optimise their processes and respond swiftly to changing demands in the market, such as scale up or down their production lines.
Conclusion
IONA can help automotive manufacturers adopt a cellular manufacturing process by unlocking a flexible and efficient way to produce a variety of composite components. IONA’s ability to quickly and accurately align tooling, eliminates the need for dedicated cells, machinery and highly skilled operators for low-mix production, which can save manufacturers significant operational and capital expenditure. Additionally, IONA’s flexibility allows manufacturers to make on-the-fly adjustments to their production schedule, which can help them to respond quickly to changes in demand.

Andy Silcox, Research Director, AMRC Cymru
James Allum, Senior Manufacturing Research Engineer, AMRC Cymru
Dr Stuart Morris, Engineering Director, Pentaxia


